Type de publics: General
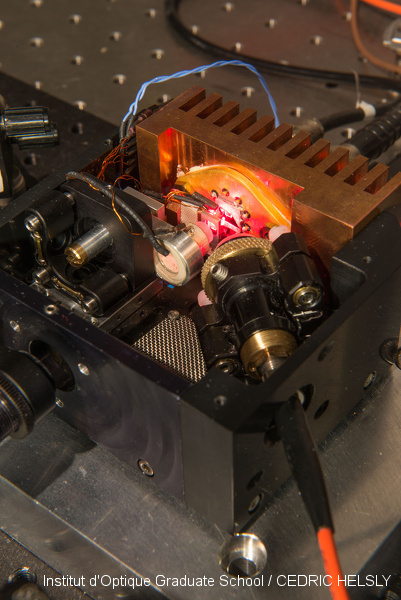
Bifrequency laser
Within the ANR-funded 2POLEVF project, a two-frequency laser prototype was developed, et manufactured at SYRTE. The cavity length is 10 mm. The laser cavity includes birefringent components (polarization beam splitter, electro-optical crystal) and an etalon. The pump source is a fiber-coupled laser diode at 670 nm. The whole setup is compact and integrated in a 90 x 90 x 40 mm^3 casing.
This project has been funded with support from FIRST-TF.
http://phototheque.institutoptique.fr/picture.php?/7911/category/352
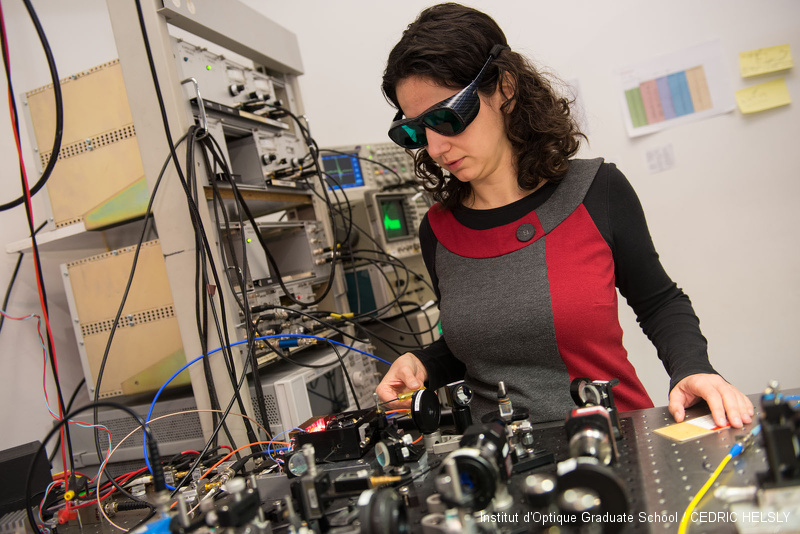
Bifrequency laser
Fabiola Camargo and Paul Dumont worked together at LCF for the development and characterization of a two-frequency laser source designed for a CPT atomic clock. The laser source was designed and studied with the ANR-funded project 2POLEVF, in collaboration with C2N, LAC, LCF, SYRTE, TRT. The laser source is a Vertical Extended-Cavity Surface Emitting Laser, which is optically pumped with a high power laser diode at 670 nm. The optical bench allows to stabilize the optical frequency on an atomic transition, and the frequency difference on a local oscillator.
This project has been funded with support from FIRST-TF.
http://phototheque.institutoptique.fr/picture.php?/7913/category/352
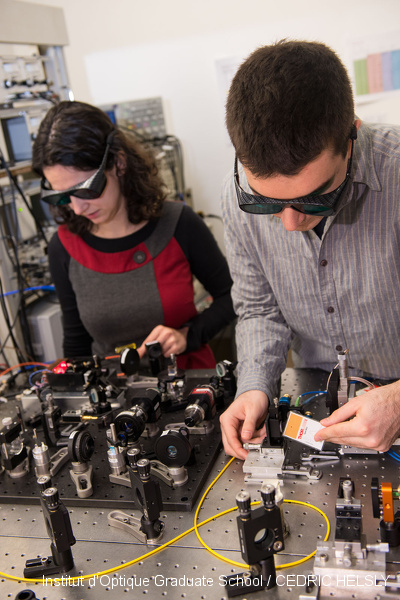
Bifrequency laser
Fabiola Camargo and Paul Dumont worked together at LCF for the development and characterization of a two-frequency laser source designed for a CPT atomic clock. The laser source was designed and studied with the ANR-funded project 2POLEVF, in collaboration with C2N, LAC, LCF, SYRTE, TRT. The laser source is a Vertical Extended-Cavity Surface Emitting Laser, which is optically pumped with a high power laser diode at 670 nm. The optical bench allows to stabilize the optical frequency on an atomic transition, and the frequency difference on a local oscillator.
This project has been funded with support from FIRST-TF.
http://phototheque.institutoptique.fr/picture.php?/7921/category/352
Bifrequency laser
Fabiola Camargo and Paul Dumont worked together at LCF for the development and characterization of a two-frequency laser source designed for a CPT atomic clock. The laser source was designed and studied with the ANR-funded project 2POLEVF, in collaboration with C2N, LAC, LCF, SYRTE, TRT. The laser source is a Vertical Extended-Cavity Surface Emitting Laser, which is optically pumped with a high power laser diode at 670 nm. The optical bench allows to stabilize the optical frequency on an atomic transition, and the frequency difference on a local oscillator.
This project has been funded with support from FIRST-TF.
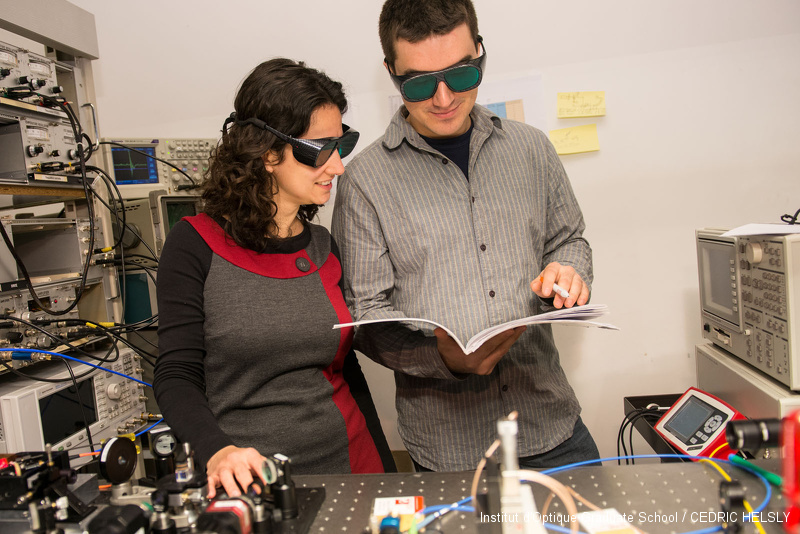

http://phototheque.institutoptique.fr/picture.php?/7921/category/352
The new masters of time
Fifty years ago, on October 13, 1967, marked the first time the second, the unit of time, was defined not by stars but by atoms. In this quest for precision, today’s scientists are now inventing the clocks of tomorrow, which will not only be able to express time with even more accuracy, but may also revisit the fundamental laws of physics.
The economic impact on the UK of a disruption to GNSS
Like all modern economies, much of everyday life in the UK is reliant on Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS). It is sometimes called the invisible utility.
GNSS provide signals from satellites orbiting in space to give us accurate information on positioning, navigation and timing. These systems have a large range of uses but, until now, the economic benefits haven’t always been well understood. It is not clear what the economic impact of a GNSS outage would be on the UK.
This report looks at what would happen to the UK economy if GNSS were unavailable for 5 days.
https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/the-economic-impact-on-the-uk-of-a-disruption-to-gnss
The Impact of quantum technologies on the EU’s future policies: Part 1 Quantum Time
Atomic clocks are a quantum technology, used in national metrology laboratories to define UTC and in various networked infrastructure. Developments in the clocks themselves, and in the distribution of precise time, can be expected to affect several application areas of importance to European policy.
Refonte annoncée du Système International d’Unités : enjeux et perspectives
Le système global de mesure qui repose sur le Système International d’Unités (SI) est le cadre actuel assurant la fiabilité et l’exactitude des mesures au niveau international. Un tel système de mesure, transnational et réellement global est indispensable au commerce, à l’industrie et donc développement de nos sociétés modernes. En 2018 le Comité International des Poids et Mesures (CIPM) prévoit de redéfinir le SI. Cette redéfinition consistera principalement à fixer la valeur d’un jeu de constantes fondamentales dimensionnées (la valeur de la constante de Boltzmann kB, par exemple, sera fixée pour redéfinir le kelvin). Cette réforme profonde de notre système de mesure qui reposera sur les meilleures déterminations des constantes fondamentales a pour objectif la mise en place d’un SI plus simple et plus cohérent.
Après un rappel historique sur l’évolution du système d’unités, de la Révolution française à nos jours, nous présentons les enjeux et perspectives de la refonte annoncée du Système International d’Unités.
Les Références de temps et d’espace
Un panorama encyclopédique : histoire, présent et perspectives
Les systèmes de navigations par satellite tels que GPS ou le futur système européen Galileo offrent un éventail impressionnant de possibilités nouvelles aussi bien au grand public qu’aux professionnels (navigateurs, topographes…). L’évolution du niveau des mers est un paramètre-clé du changement climatique, tant pour sa compréhension que pour son impact sociétal. L’exploration planétaire par les missions spatiales produit un nombre croissant de résultats pour la connaissance de notre Système solaire. La vérification et l’amélioration des théories de la gravitation est actuellement une activité importante de la Physique fondamentale.
Un facteur commun est sous-jacent à tous ces constats : le rôle crucial des références de temps et d’espace. C’est l’ambition de cet ouvrage que d’offrir une brève encyclopédie sur ce domaine. Partant d’un panorama historique qui insiste sur l’évolution des concepts, il aboutit à une présentation de l’état actuel, illustrant le rôle majeur des techniques spatiales, et surtout des horloges atomiques qui placent le temps comme élément fondamental sur le plan métrologique.
A Software-Defined GPS and Galileo Receiver
A Single-Frequency Approach
Satellite navigation receivers are used to receive, process, and decode space-based navigation signals, such as those provided by the GPS constellation of satellites. There is an increasing need for a unified open platform that will enable enhanced receiver development and design, as well as cost-effective testing procedures for various applications. This book provide hands-on exploration of new technologies in this rapidly growing field.
One of the unique features of the work is the interactive approach used, giving readers the ability to construct their own Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) receivers. To construct such a reconfigurable receiver with a wide range of applications, the authors discuss receiver architecture based on software-defined radio (SDR) techniques. The presentation unfolds in a systematic, user-friendly style and goes from the basics to cutting-edge research.
